Water-Efficient Landscaping in Saudi Arabia: A Sustainable Oasis in the Desert
Saudi Arabia, a nation synonymous with vast deserts and scorching temperatures, faces an inherent challenge: water scarcity. With limited freshwater resources and a rapidly growing population, sustainable water management has become a paramount concern.
In this context, water-efficient landscaping emerges not merely as an aesthetic choice but as a critical environmental and economic imperative. Traditional landscaping practices, often reliant on exotic, water-intensive plants, are unsustainable in such an arid climate.

This article delves into the transformative shift towards water-efficient landscaping in Saudi Arabia, exploring its principles, benefits, key techniques, and the innovative projects leading the way in creating a greener, more sustainable future for the Kingdom.
The Imperative for Water Efficiency in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia’s climate is characterized by extreme heat and minimal rainfall, making water a precious commodity. The majority of the country’s water supply comes from non-renewable groundwater sources and energy-intensive desalination plants.
As urbanization and development accelerate, the demand for water continues to rise, placing immense pressure on these finite resources. Landscaping, while contributing to urban aesthetics and quality of life, can be a significant consumer of water if not managed efficiently. Therefore, adopting water-efficient landscaping practices is crucial for:
•Water Conservation: Directly reducing the demand for potable water, thereby preserving precious groundwater reserves and lessening the burden on desalination infrastructure.

•Environmental Sustainability: Minimizing the ecological footprint associated with water extraction and treatment, and promoting biodiversity through the use of native and drought-tolerant plant species.
•Economic Prudence: Lowering water bills for individuals and organizations, and reducing the operational costs associated with water supply and wastewater treatment at a national level.
•Resilience Building: Creating landscapes that are better adapted to the harsh desert environment, requiring less maintenance and proving more resilient to climate change impacts.
Principles of Water-Efficient Landscaping
Water-efficient landscaping, often referred to as xeriscaping, is a comprehensive approach to designing, installing, and maintaining landscapes that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation. While the term xeriscaping might evoke images of barren, rock-filled gardens, modern xeriscaping embraces lush, vibrant designs that thrive with minimal water. The core principles include:

1.Planning and Design: Thoughtful design is the cornerstone of water-efficient landscaping. This involves analyzing the site’s conditions, including sun exposure, soil type, and drainage, and then creating a landscape plan that groups plants with similar water needs together (hydrozoning). This allows for efficient irrigation and prevents overwatering of drought-tolerant species.
2.Soil Improvement: Healthy soil is crucial for water retention. Incorporating organic matter, such as compost, improves soil structure, increases its water-holding capacity, and promotes healthy root growth, reducing the need for frequent watering.
3.Efficient Irrigation: Moving away from traditional, wasteful irrigation methods is key. This includes:
•Drip Irrigation: Delivering water directly to the plant’s root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff. As highlighted by AZUD, subsurface drip irrigation systems can lead to up to 30% water savings [2].
•Smart Irrigation Systems: Utilizing sensors and weather data to automatically adjust irrigation schedules based on real-time plant needs and environmental conditions. These systems ensure water is applied only when and where it’s needed.
4.Appropriate Plant Selection: Choosing native and drought-tolerant plants is perhaps the most impactful principle. These plants are naturally adapted to the local climate and require significantly less water once established. Dar Al-Handasah’s project in KAFD successfully utilized native, drought-tolerant species, contributing to a 59% reduction in water use [1].
5.Mulching: Applying a layer of organic or inorganic mulch around plants helps retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. This reduces evaporation from the soil surface and keeps roots cooler.
6.Reduced Turf Areas: Lawns are typically the most water-intensive part of a landscape. Minimizing turf areas, especially in arid regions, or replacing them with drought-tolerant groundcovers, permeable hardscapes, or xeriscape plantings can drastically reduce water consumption.
7.Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance, such as proper pruning, weeding, and checking irrigation systems for leaks, ensures the long-term success of a water-efficient landscape.
Key Techniques and Innovations in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is actively embracing various techniques and innovations to promote water-efficient landscaping, driven by both environmental necessity and ambitious national development plans like Vision 2030. Some of the prominent approaches include:
Xeriscaping: The Art of Dry Landscaping
Xeriscaping, as a holistic approach, is gaining significant traction across the Kingdom. It involves designing landscapes that require little or no irrigation beyond natural rainfall. The King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) has been a pioneer in this regard, converting over 100 sites to xeriscaping themes, which inherently demand minimal water .
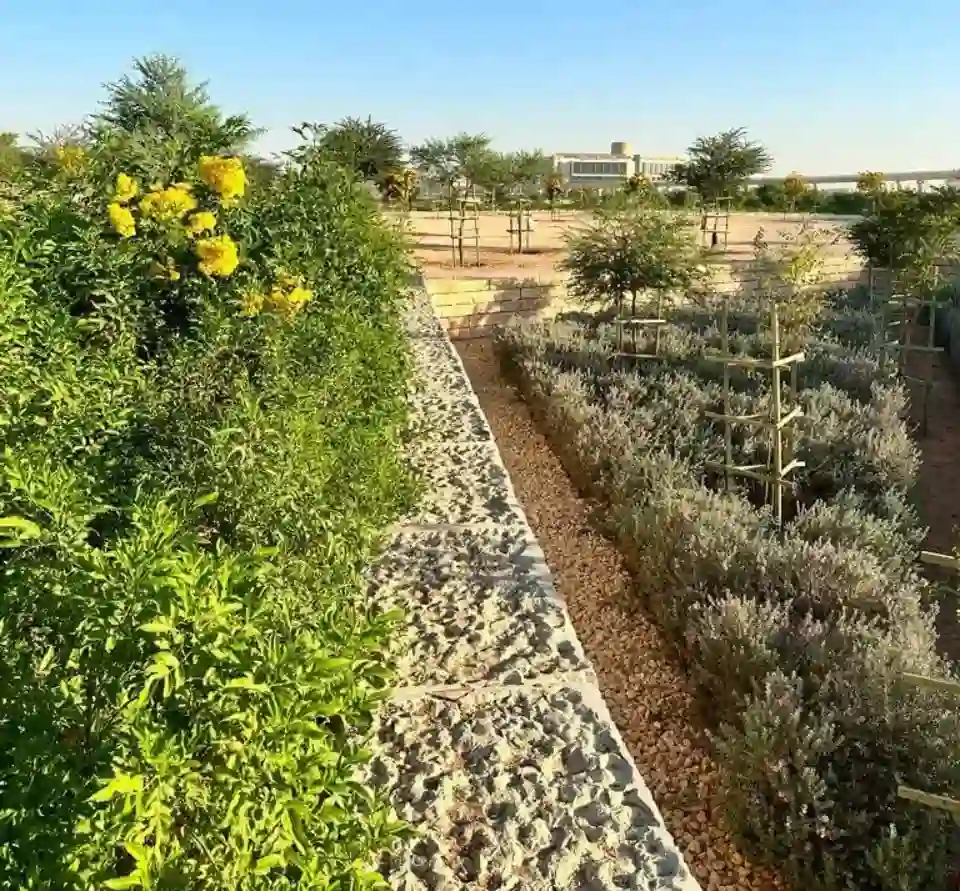

The benefits of xeriscaping extend beyond water conservation, encompassing reduced maintenance, lower energy consumption (due to less pumping and treatment of water), and the promotion of local biodiversity.
Advanced Irrigation Technologies
The adoption of smart irrigation systems and high-efficiency technologies is transforming water management in Saudi Arabian landscapes. These systems leverage technology to optimize water delivery:

•Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI): This method, as highlighted by AZUD, delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff. It’s particularly effective in arid climates where surface evaporation is high .
•Sensor-Based Systems: Soil moisture sensors, weather stations, and evapotranspiration (ET) controllers are integrated into irrigation systems to provide real-time data. This allows for precise watering schedules, ensuring plants receive only the water they need, when they need it.
•Pressure-Compensating Emitters: These emitters ensure uniform water distribution across the landscape, regardless of changes in water pressure, preventing overwatering in some areas and underwatering in others.
Water Recycling and Reuse
Given the scarcity of fresh water, Saudi Arabia is increasingly investing in water recycling and reuse initiatives for landscaping purposes. Treated Sewage Effluent (TSE) is a prime example.

KAUST has successfully converted its potable irrigation network to TSE, resulting in a nearly 40% reduction in irrigation water usage, with approximately 40% of their landscape irrigation water now sourced from the TSE network . This not only conserves potable water but also provides a sustainable solution for wastewater management.
Native and Drought-Tolerant Plant Species
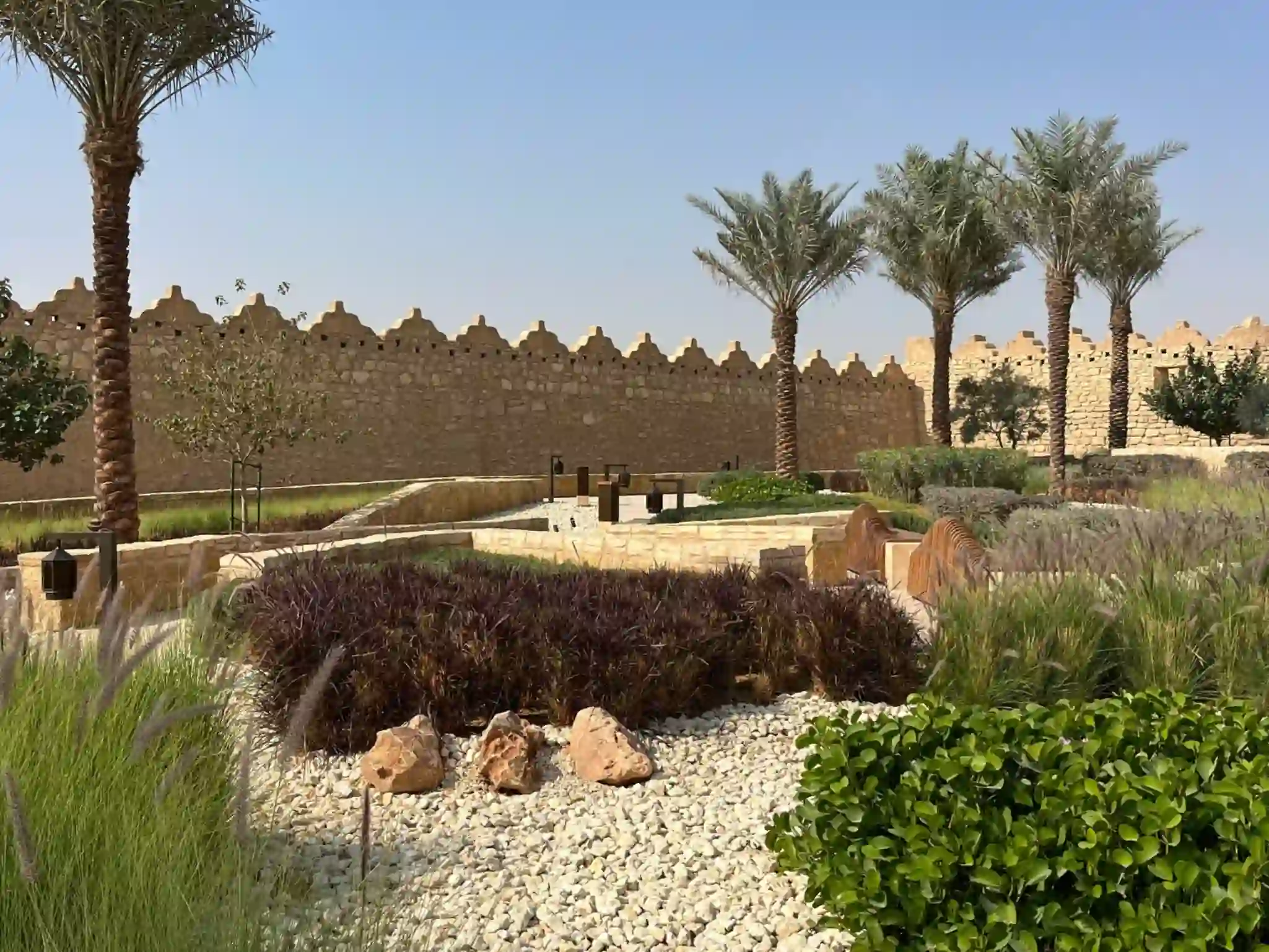
The strategic selection of plant species is fundamental to water-efficient landscaping in Saudi Arabia. Emphasis is placed on using native plants that are naturally adapted to the desert climate and require minimal supplemental irrigation.
Examples include various species of palms, acacia, ghaf, and other indigenous shrubs and groundcovers. Beyond native species, a wide range of drought-tolerant ornamental plants are also being utilized to create aesthetically pleasing and sustainable landscapes.
Impact and Future Outlook
The shift towards water-efficient landscaping in Saudi Arabia is yielding significant positive impacts. Projects like the King Abdullah Financial District (KAFD) have demonstrated remarkable water savings, with an average reduction of 59% in total water use across three parcels due to efficient design and technologies [1]. These successes serve as powerful case studies, inspiring further adoption across the Kingdom.
The future of landscaping in Saudi Arabia is undoubtedly water-efficient. With continued government support, technological advancements, and increasing public awareness, the principles and practices of sustainable landscaping will become even more ingrained.
The ongoing mega-projects, such as NEOM and the Red Sea Project, are incorporating water-efficient landscaping as a core component of their design, setting new benchmarks for sustainable development in arid environments. This commitment to water conservation through innovative landscaping is transforming Saudi Arabia’s urban and natural environments, creating a sustainable oasis in the desert.
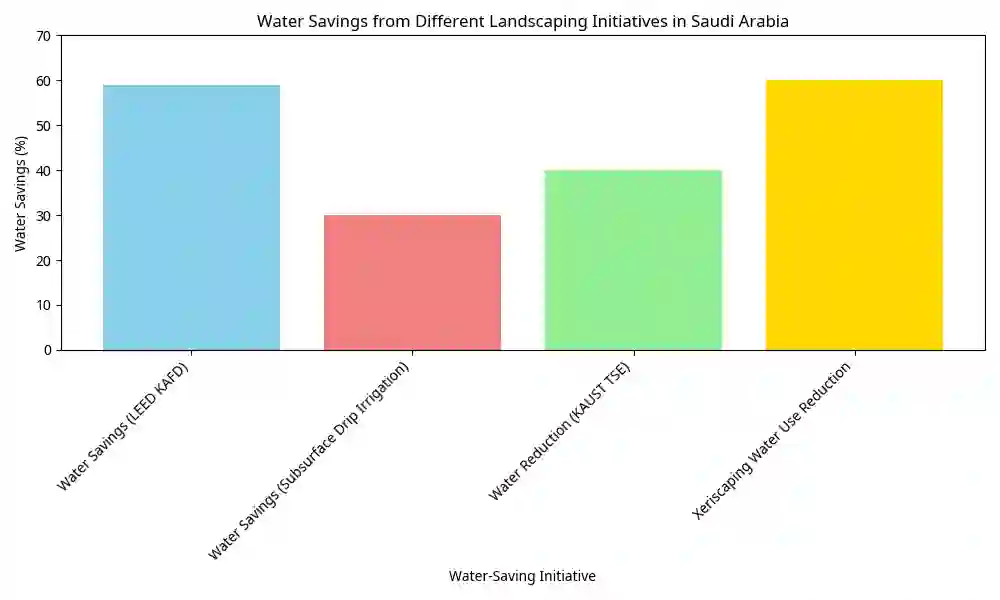
Facts and Figures: Water Savings in Saudi Arabian Landscaping
To illustrate the tangible benefits of water-efficient landscaping, here’s a summary of water savings achieved through various initiatives:
| Aspect | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Water Savings (LEED KAFD) | Average 59% | Dar Al-Handasah (KAFD Project) |
| Water Savings (Subsurface Drip Irrigation) | Up to 30% | AZUD (Sub-surface Drip Irrigation) |
| Water Reduction (KAUST TSE) | Nearly 40% | KAUST (TSE Network) |
| Xeriscaping Water Use Reduction | Up to 60% or more | ResearchGate |
Visualizing Water Savings
Below is a graphical representation of the water savings achieved by different water-efficient landscaping initiatives in Saudi Arabia:
Conclusion
Water-efficient landscaping is more than just a trend in Saudi Arabia; it is a fundamental shift towards a sustainable future. By embracing principles such as thoughtful design, efficient irrigation, and the use of native and drought-tolerant plants, the Kingdom is transforming its landscapes into resilient, water-wise environments.
The successful implementation of these practices in major projects demonstrates a clear path forward for conserving precious water resources, fostering environmental stewardship, and creating aesthetically pleasing spaces that thrive in the desert climate. As Saudi Arabia continues its journey towards Vision 2030, water-efficient landscaping will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in building a greener, more sustainable, and water-secure nation.